Programmable Barcode Scanners:
Uses, Creation and How it Differs from Configurable Scanners
The Barcode Boom
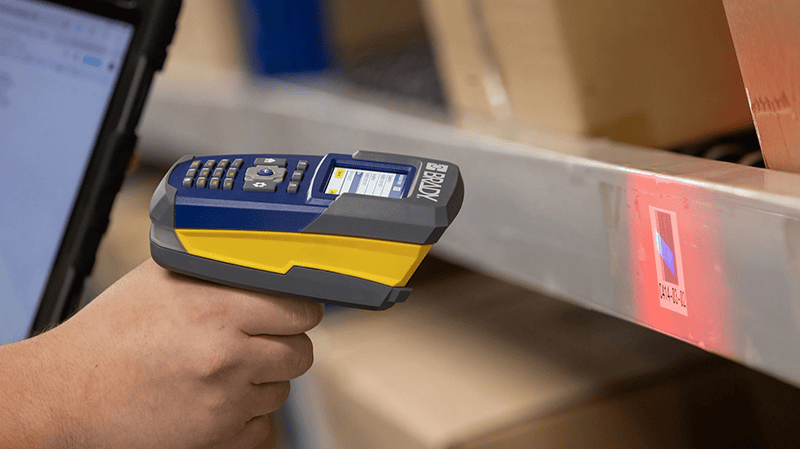
Barcode scanners are the tool that makes your life easier.
Currently, one of the hottest devices globally, the barcode scanner industry is booming. Barcode scanners connect what’s happening on the shop floor to supply chains, shipping and receiving, and inventory in warehouses. To businesses worldwide, barcode scanners are no longer just nice to have. They’re an essential part of operations, saving time, money and labor while creating greater efficiencies each time they’re used — especially if they’re programmable.
Here’s how they help businesses:
-

Manage assets and inventory
-

Capture shipping and receiving data
-

Identify products
-

Reduce human errors
-

Track raw materials, work in process items, batches, samples and finished products
-

Increase efficiency and effectiveness of operations
Plus, they help prevent errors and keep people safe. A recent barcode and healthcare practices study found that barcode technology reduced errors in patient drug dispensing up to 96%.1
The drive to digitize
From healthcare to logistics, warehousing to e-commerce, the list of industries that rely on barcodes is growing. According to Future Market Insights (FMI), the barcode scanner boom is largely caused by the emerging Industry 4.0 and the drive to digitize.2
More and more, real-time information is needed to make critical decisions about inventory, supply chains and labor — 3 pillars that really affect the health of modern businesses.
Establishing a robust barcode system and using industrial-grade programmable scanners will give you the capabilities to tackle your most complex operations – seamlessly.
What makes a scanner programmable?
Though most barcode scanners have configuration settings that can be adjusted, not all can be programmed for high-level functions such as executing custom code or automating functions. Let’s look at scanners that are configurable and programmable.
Configurable barcode scanners
These scanners can be programmed to change the way the device operates and reads barcode types (symbologies):
- Languages
- Illumination
- Time stamp settings
- Trigger functions
- Sounds
- Volume
- Auto sensing
- 1D or 2D barcodes
Programmable barcode scanners
Programmable scanners are the go-to for industrial barcode applications as they offer the widest range of capabilities:
- Are highly customizable
- Execute custom code to perform barcode operations
- Integrate easily with other systems
- Can be programmed per application
- Provide automation options
- Offer a great deal of flexibility in workflows
Besides integrating with other systems (such as an inventory management software), programmable scanners can be customized — almost infinitely — for nearly any application. Labs use them for tracking patient samples. Electronics manufacturing uses them for QA checks. Warehouses use them to manage inventory. And, the majority of businesses use them for data automation.
How do barcode scanners and readers work?
Although there are different types of identification technology, industrial applications rely heavily on optical image technology because they can read both 1 and 2-dimensional barcodes.
Optical Barcode Scanners
As the name suggests, a barcode scanner reads a printed barcode with a lens and red light beam, or an image scanner takes a picture. Then, it decodes it and sends the data string to a computer.
RFID Readers
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) readers use radio frequency waves to identify items and transfer data. They work in a system that consists of a reader, antenna, labels or tags, and software to translate the data. RFID scanners provide real-time feedback — without using a direct line of sight.
Which device you use depends largely on the application. Optical scanners need a direct line of sight to scan each barcode. The process takes a little more time and effort as scans are done individually. Visualize a worker picking up an item or running it under a scanner. With RFID technology, you can read multiple items quickly from greater distances.
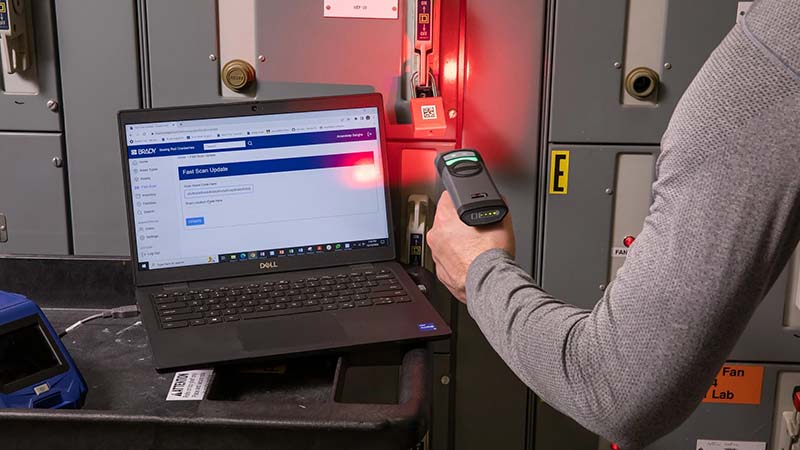
How are barcode scanners programmed?
A Barcode Scanner program is simply a set of instructions directing the scanner to record, parse, format, modify or enhance barcode data in specific ways.
Those instructions can be low-level changes to the scanner system (making a ‛beep’ sound to verify a scan) or higher-level changes (writing code to parse data) to allow scanners to interface with other systems.
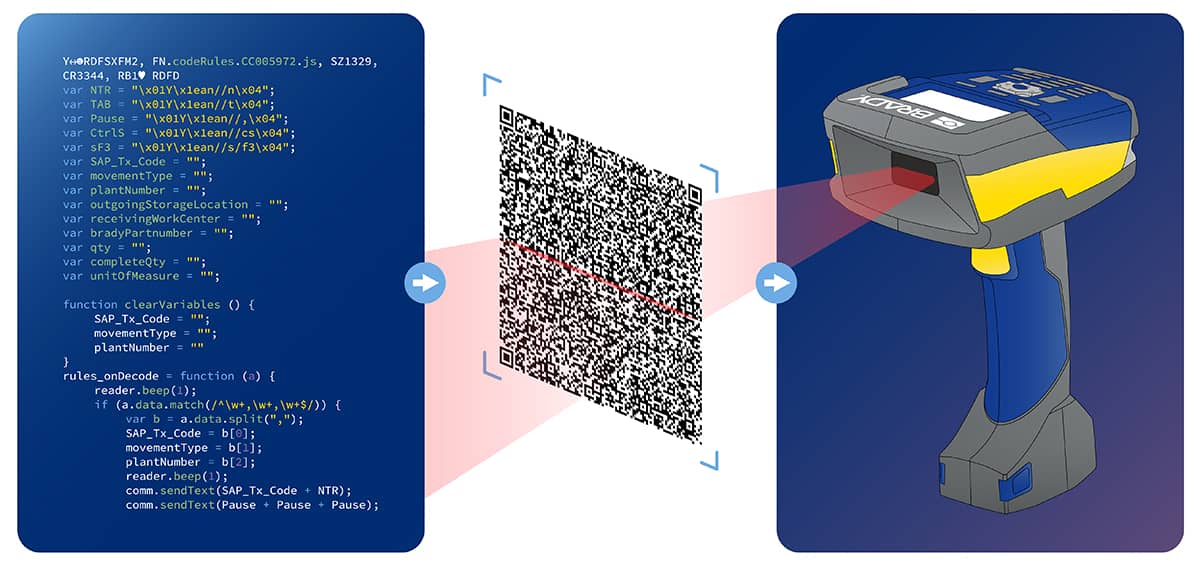
The most common way to program a scanner is to write the instructions in a programming language, such as Javascript, and then create a 2-dimensional barcode representing that programming text. As the barcode scanner scans and decodes the programming barcode it loads that new set of instructions into its memory. Here’s an example of how it works:
Barcode use in industrial applications
Now that you know the basic types of barcode scanners, their benefits and how to program them, you’ll need to consider how you’ll use them in your workflows. Common applications include:
- Tracking – Track parts, lots and batches throughout various stages of production
- Inventory - Track inventory easier and faster with a barcode inventory system that eliminates errors.
- Data automation – Accurately capture, identify, verify and transfer data
- In manufacturing facilities – Collect data in real time and connect it to software and analytics
- Packaging – Identify packages with barcodes showing country of origin, dates and batch numbers
- Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) systems – Replenish stock automatically using barcodes. Read the case study
- Distribution – Monitor shipments every step of the way
- Warehouses – Picked products can be verified by workers and taken out of inventory
- Supply chains – Track products and prevent both out-of-stocks and overstocks
How do I create a barcode system?
Let’s say you want to start using barcodes to better manage your inventory. Before you think about purchasing a scanner, you’ll need to consider how your new system will operate internally and externally (if you work with outside partners).
Define your barcode needs
How many SKUs will need barcodes?
Think about the supply chain
Do you need to align your scanning system by using the same types of barcodes?
Identify which processes need to integrate with your new barcode system
Which existing systems and software platforms does the barcode system need to interface with?
Decide on symbologies
Will you be using 1D or 2D barcodes, UPC Codes, QR Codes or industry-specific barcodes?
Choose which type of scanner or reader you’ll be using
Does your barcode application require single scans or batches? Do you need long-range visibility?
Select a printer and labels that suit your application
Do you need to print your own labels? What conditions will your labels need to endure and still stay scannable?
How Brady can help
Discover more ways you can connect it all — from the shop floor to the cloud — with Brady. We’ll help you meet your Industry 4.0 goals with customized solutions for:
- Asset tracking – Make products visible and get real-time status updates
- Inventory management – Forecast, organize and scale across facilities
- Tracking Work in Progress – Get immediate insights and faster adjustments