What is RFID?
A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Its Components, Applications and Future
Sure, you’ve heard of RFID. But what exactly is it?
More than just a type of technology, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a revolutionary force in our modern digital world. It shapes how businesses operate – adding efficiencies, streamlining operations and boosting overall productivity.
If you’d like to know more about RFID technology – what it is, how it works, its components, applications, advantages, limitations and future uses – read on. This article will help you understand just why RFID is so important to the global digital transformation.
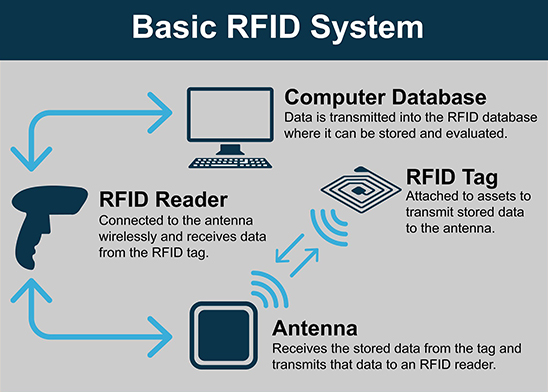
How does RFID work?
Part of RFID’s popularity lies in its ability to identify and track objects or individuals easily through small electronic devices called RFID tags or transponders. Depending on the form factor of an RFID tag, it can also be referred to as an RFID label. These tags consist of an integrated circuit and an antenna (sometimes called an inlay), which receive and transmit information. A real-world example is inventory tracking in a warehouse. Tags that are placed on products or pallets can be read with an RFID reader and entered or deleted quickly and accurately from inventory.
Types of RFID
There are many different types of tags that can optimize operations. Each has its own unique characteristics and applications:
Active RFID tags
These tags have their own power source and can actively transmit data to RFID readers. Applications include tracking high value items like cargo containers and construction machinery.
Passive RFID tags
These tags do not have a built-in power source and rely on energy harvested from the RFID reader's radio waves. Applications include product tracking and supply chain monitoring.
Semi-passive RFID tags
These tags combine the features of both passive and active tags. Applications include tracking assets and monitoring the environment (such as temperature) during storage or transportation.
Dual-frequency RFID tags
These tags allow for communication in multiple frequency bands. Applications include supply chain management and authentication of assets.
Smart labels
These labels integrate RFID technology with functions such as moisture or temperature sensing printable labels, enabling advanced data capture and identification capabilities. Applications include inventory management and supply chain tracking.
But, labels and tags are only one part of RFID technology. An RFID reader is needed to transmit radio signals to the tags and then to receive the information they contain. RFID readers, also known as interrogators, are responsible for transmitting radio signals to the tags and receiving the information they contain. RFID readers can be classified based on frequency, such as low-frequency (LF), high-frequency (HF), near field communication (NFC) ultra-high-frequency (UHF) and ultra wide band (UWB).
RFID applications
If you’re wondering how widespread RFID technology is, just about every industry uses it. Healthcare, logistics, manufacturing, agriculture and transportation are just a few examples. RFID tags and readers communicate accurate amounts and locations of items, either finished or in process.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, RFID plays an important role in patient safety. It can help identify patients and track medication. RFID-enabled systems also help providers access patient information quickly and reduce errors – two must-haves for improving overall quality of care. Hospitals and clinics have found that RFID readers and tags facilitate better inventory management, too. On medical supplies and equipment, RFID tags show if supply levels are low or which piece of equipment needs maintenance.
Logistics
The logistics sector benefits greatly from RFID's ability to track and trace goods throughout the supply chain. This technology can optimize operations and reduce losses. With RFID-enabled systems, logistics companies can gain real-time visibility into their inventory, streamline warehouse management and improve shipping and delivery processes.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Intelligent Manufacturing
RFID plays a vital role in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and intelligent manufacturing initiatives. It provides real-time asset tracking, predictive maintenance and process automation. With RFID technology, manufacturers can meet their goals with greater efficiency, reduced downtime and enhanced quality control.
RFID integration
The integration of RFID into existing infrastructure offers seamless connectivity and data exchange between devices and systems. This can enhance overall efficiency and decision-making. For example, RFID technology can be integrated into access control systems, enabling secure and automated entry to buildings or restricted areas.
Advantages of RFID systems
RFID technology brings several advantages to businesses and industries:

Improved operational efficiency

Accelerated supply chain processes

Enhanced asset tracking

Real-time data

Better inventory management and bulk reading
RFID technology improves operational efficiency in a variety of ways: automating data capture, reducing manual processes and eliminating human errors. It also increases productivity and cost savings by accelerating supply chain processes and enhancing asset tracking capabilities. Using real-time data provided by RFID technology allows for better decision-making and improved responsiveness to customer demands.
Another advantage of RFID is its ability to enhance inventory management. Traditional barcode systems require line-of-sight scanning, while RFID allows for non-line-of-sight and bulk reading. This means that multiple items can be scanned simultaneously, reducing the time and effort required for inventory management tasks. RFID-enabled systems can also provide accurate and real-time inventory data, reducing stockouts and improving replenishment processes.
Disadvantages of RFID Systems
Despite the numerous advantages, there are certain limitations associated with RFID technology. One concern is the initial cost of implementing RFID systems. While the prices of RFID tags and readers have significantly decreased over the years, there may be substantial upfront investments required – especially for large-scale deployments. However, it is important to consider the long-term benefits and potential cost savings that RFID technology can bring – especially with different technologies such as passive and active RFID.
Another challenge is the read range limitation of some RFID tags – mainly, passive tags. The distance over which passive RFID tags can be read is relatively short compared to active tags. This limitation may require businesses to strategically place RFID readers throughout their operations to ensure optimal tag detection. Additionally, some environmental factors may affect RFID performance, necessitating careful planning and management.
The future of RFID
The future of RFID technology is promising, with several emerging trends and potential applications on the horizon. Advancements in miniaturization and cost reduction will drive wider adoption of RFID in smaller objects and consumer goods. As technology continues to evolve, RFID tags may become even more discreet and seamlessly integrated into everyday items.
The integration of RFID with other emerging technologies can unlock new possibilities. For example, combining RFID with sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) platforms will enable real-time environmental monitoring, asset health tracking and predictive maintenance. Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms can be applied to RFID data, providing actionable insights and facilitating intelligent decision-making.
In the future, RFID technology may increase transparency and accountability in food safety and product authenticity. This can be accomplished by tracking and tracing products throughout the supply chain.
In the healthcare sector, RFID will continue to evolve, facilitating real-time patient monitoring, medication adherence and personalized healthcare solutions. Other patient-related solutions include RFID-enabled wearable devices and smart healthcare systems that will be able to monitor patients remotely, detect health issues earlier and enable timely interventions. These RFID-enabled solutions will provide healthcare professionals with accurate and up-to-date patient data, allowing for personalized and proactive care.
How Brady can help
If you’re ready to unlock your next level of productivity, Brady can help. As a trusted partner, we can support you every step of the way – pairing advanced technologies with your existing system. Together, we can connect your facility so you can optimize your operations. Track assets better. Improve inventory management. Use high-performance hardware and software, plus RFID labeling technologies to custom-build a solution that fits your future.